Subscribe to Automate Avenue: Your 5-minute brief on Automating your business & get our latest templates
Tired of answering the same support emails? This AI workflow reads your knowledge base and automatically drafts email replies, handling customer questions for you.
Topic: Business Support
Platform: N8N
Original Author: Bernhard Hauser
Workflow Template:
Key Takeaway
Automated Email Support for Enhanced Efficiency: This workflow demonstrates how to leverage AI within an automation platform to handle customer support email inquiries efficiently.
By automating the process of checking for new emails, understanding user questions, extracting relevant information from a knowledge base, and drafting responses, this system significantly reduces the manual workload associated with email support. It offers a streamlined approach to providing timely and accurate support, even when customers bypass readily available self-service resources.
The integration of a confidence assessment and human approval step ensures a balance between automation and quality control, making it a practical solution for businesses seeking to optimize their support operations.
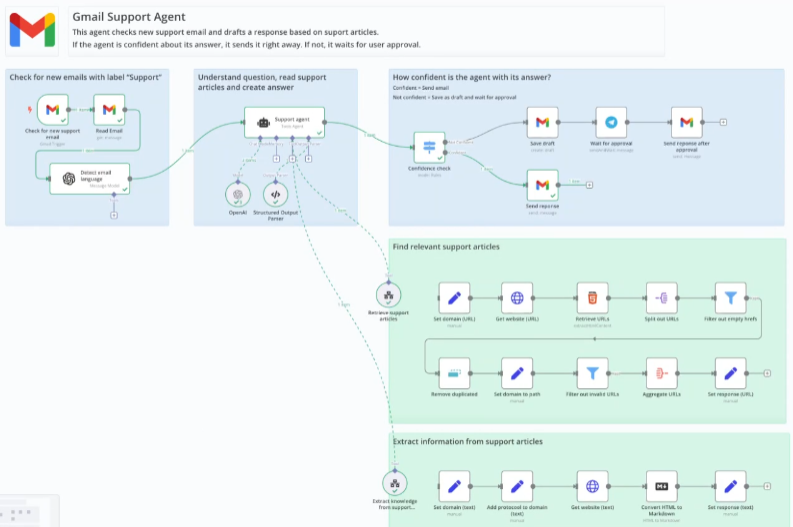
Overview of the N8N Workflow
This workflow is designed to automate the handling of customer support requests received via email, specifically using an AI agent integrated within the n8n automation platform. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Monitoring for New Support Emails:
- Trigger: The workflow begins by continuously monitoring a designated email inbox (like a Gmail account) for new incoming emails.
- Functionality: This step involves setting up an email trigger node within n8n that is configured to check the inbox at regular intervals.
- Content Extraction: Once a new email is detected, the workflow automatically reads and extracts the email’s content, including the subject line and body text.
- Language Detection: The workflow also includes a feature to detect the language of the email. This is important for ensuring that subsequent AI processing and knowledge base searches are conducted in the appropriate language, improving accuracy and relevance of responses.
2. Understanding the Question and Finding Relevant Support Articles:
- AI-Powered Analysis: This is a crucial step where an AI model is employed to analyze the content of the support email.
- Intent Recognition: The AI is designed to understand the user’s question or issue within the email text. This involves natural language processing (NLP) to identify keywords, context, and the overall intent behind the message.
- Knowledge Base Search: Based on the identified intent, the workflow then interacts with a pre-existing knowledge base (e.g., a collection of help articles). It searches this knowledge base for articles that are relevant to the user’s question. This search is likely conducted using keywords and semantic matching techniques to ensure the most pertinent articles are retrieved.
- Structured Data Extraction (for Response Formulation): The system aims to extract specific data points or key pieces of information from the identified knowledge base articles that can be used to formulate a direct answer to the user’s question. This focuses on getting the specific information needed to answer the email, not just the entire article.
3. Extracting Information from Support Articles and Structuring Data:
- HTML to Markdown Conversion: Knowledge base articles are often stored in HTML format. To make them easier for the AI to process and understand, the workflow includes a step to convert the HTML content of the relevant articles into Markdown text. Markdown is a simpler, more readable format for AI interpretation and text manipulation.
- Structured Format: The extracted information, now in Markdown, is further processed to organize it into a structured format. This might involve identifying key sections, bullet points, or specific answers within the article and arranging them in a way that is readily understandable by the AI for response drafting. This structured format also aids in making the response more coherent and direct.
4. Confidence Assessment of the Response:
- AI Confidence Score: Before automatically sending a response, the workflow incorporates a confidence assessment mechanism. This involves the AI evaluating how confident it is in the relevance and accuracy of the drafted response based on the extracted knowledge base information.
- Threshold for Automation vs. Human Review: A confidence threshold is likely set within the workflow. If the AI’s confidence score is above this threshold, the workflow proceeds to automatically send the email response (step 5a). However, if the confidence score is below the threshold, it indicates that the AI is less certain about the response’s accuracy or completeness, and the workflow will then defer to human review (step 5b).
5. Sending or Approving the Response (Handling Automation vs. Human Oversight):
5a. Automated Sending (High Confidence):
- Direct Email Reply: If the AI’s confidence is high enough, the workflow proceeds to automatically draft an email response based on the structured information extracted from the knowledge base.
- Sending the Email: The drafted email is then automatically sent as a reply to the original support request email, directly from the designated support email address.
5b. Draft for Human Approval (Low Confidence):
- Draft Email Creation: If the AI’s confidence is low, instead of automatically sending, the workflow saves the drafted response as a draft email in the support email account’s drafts folder.
- Notification for Review: The system then triggers a notification to a human agent to review the drafted email. This notification could be sent through various channels, like a messaging platform or email.
- Human Review and Approval/Editing: A human agent then reviews the drafted email, ensuring its accuracy, completeness, and appropriate tone. They have the option to edit the draft if needed.
- Manual Sending (Post-Approval): Once the human agent is satisfied with the draft, they can manually approve and send the email response. This ensures human oversight for more complex or less straightforward inquiries.
Possible Expansions of the Workflow
This workflow, focused on automating email support, can be expanded in several ways to enhance its capabilities and broaden its application, without including business or people names. Here are some possibilities:
Multi-Channel Support Integration:
- Expansion Idea: Extend the workflow to handle support requests from multiple channels beyond just email. This could include integrating with live chat platforms on websites, social media messaging, or other communication channels where customers might seek support.
- Functionality: Implement triggers for these additional channels to feed into the same AI-powered analysis and response system. This would provide a unified support automation system across various customer touchpoints.
Proactive Support and Issue Prediction:
- Expansion Idea: Move beyond reactive support to proactive issue identification and resolution.
- Functionality: Integrate monitoring of system logs, application performance data, or even customer behavior patterns (if ethically and privacy-consciously feasible) to predict potential issues before customers report them. The workflow could then proactively send out notifications or solutions to users who might be affected.
Personalized Response Generation:
- Expansion Idea: Enhance the AI’s response generation to create more personalized and context-aware replies.
- Functionality: Incorporate data about the customer (e.g., past interactions, account type, product usage history – if available and relevant within privacy constraints) to tailor the support responses. This could involve personalizing greetings, referencing past issues, or offering recommendations specific to the customer’s situation.
Sentiment Analysis and Prioritization:
- Expansion Idea: Integrate sentiment analysis to understand the emotional tone of support requests.
- Functionality: Use AI to detect the sentiment (e.g., frustration, urgency) in customer emails. This could be used to prioritize responses, escalate urgent or highly negative inquiries to human agents faster, or tailor the tone of automated responses to match the customer’s emotional state.
Continuous Learning and Improvement Loop:
- Expansion Idea: Implement a feedback loop to continuously improve the AI’s performance and knowledge base relevance.
- Functionality: Track data on human agent interventions (when they edit drafted responses or handle cases escalated due to low AI confidence). Analyze these interventions to identify areas where the AI is underperforming or where the knowledge base is lacking. Use this data to retrain the AI models and update the knowledge base, making the system more accurate and efficient over time.
Automated Escalation and Ticket Management:
- Expansion Idea: Integrate with a ticket management system to handle more complex issues and track support requests more formally.
- Functionality: For cases requiring human intervention or those that cannot be resolved with existing knowledge base articles, automatically create support tickets in a dedicated system. This allows for better tracking of unresolved issues, assignment to human agents, and monitoring of resolution times. The workflow could also automatically escalate tickets based on keywords or sentiment.
Multi-Lingual Support Expansion:
- Expansion Idea: Enhance the workflow to handle support requests in multiple languages beyond the initial language detection.
- Functionality: Integrate machine translation capabilities to translate both incoming support requests and knowledge base articles. This would enable the AI agent to provide support in a wider range of languages, expanding its reach and utility.
Integration with other Automation Workflows:
- Expansion Idea: Connect this support workflow with other business process automation workflows.
- Functionality: For example, if a support request is about a billing issue, the workflow could trigger another workflow to check the customer’s billing status in a payment processing system. Or, if it’s a technical issue, it could trigger a workflow to check system status or initiate diagnostic processes automatically. This could lead to more comprehensive and efficient resolution of customer issues.